工厂模式 简单工厂模式(静态工厂模式) 通过Factory来new一个实例,但是如果需要增加实例类的话,需要修改Factory类的代码。
主类只需要知道Factory类即可。
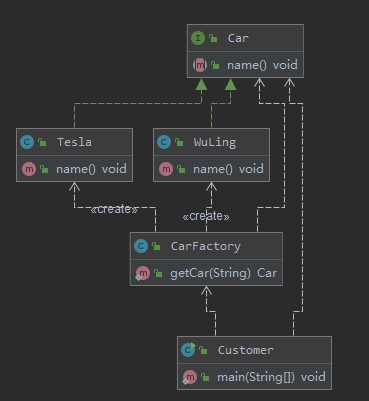
例子: UML类图如下所示
简单工厂UML类图.jpg
源码如下所示: 1 2 3 public interface Car void name () }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class Tesla implements Car @Override public void name () System.out.println("特斯拉!" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class WuLing implements Car @Override public void name () System.out.println("五菱宏光!" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class CarFactory public static Car getCar (String name) if (name == "五菱" ) { return new WuLing(); } else if (name == "特斯拉" ) { return new Tesla(); } else { return null ; } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class Customer public static void main (String[] args) Car car1 = CarFactory.getCar("五菱" ); Car car2 = CarFactory.getCar("特斯拉" ); car1.name(); car2.name(); } }
工厂方法模式 主类根据需要通过对应的工厂获得实体类。
但是但我们需要增加实体类时,需要增加类和类工厂,类文件变得很多。
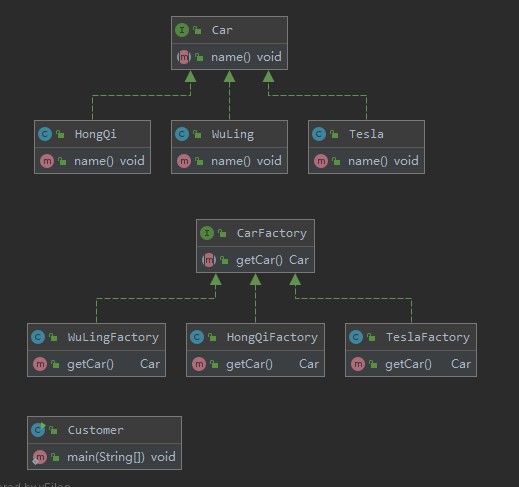
例子: UML类图如下所示:
方法工厂模式UML类图.jpg
源码如下所示: 1 2 3 public interface Car void name () }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class HongQi implements Car @Override public void name () System.out.println("红旗汽车!" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class Tesla implements Car @Override public void name () System.out.println("特斯拉!" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class WuLing implements Car @Override public void name () System.out.println("五菱宏光!" ); } }
1 2 3 public interface CarFactory Car getCar () ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class HongQiFactory implements CarFactory @Override public Car getCar () return new HongQi(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class TeslaFactory implements CarFactory @Override public Car getCar () return new Tesla(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class WuLingFactory implements CarFactory @Override public Car getCar () return new WuLing(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Customer public static void main (String[] args) Car car1 = new WuLingFactory().getCar(); Car car2 = new TeslaFactory().getCar(); Car car3 = new HongQiFactory().getCar(); car1.name(); car2.name(); car3.name(); } }
抽象工厂模式 在抽象工厂模式中,接口是负责创建一个相关对象的工厂,不需要显式指定它们的类。每个生成的工厂都能按照工厂模式提供对象。
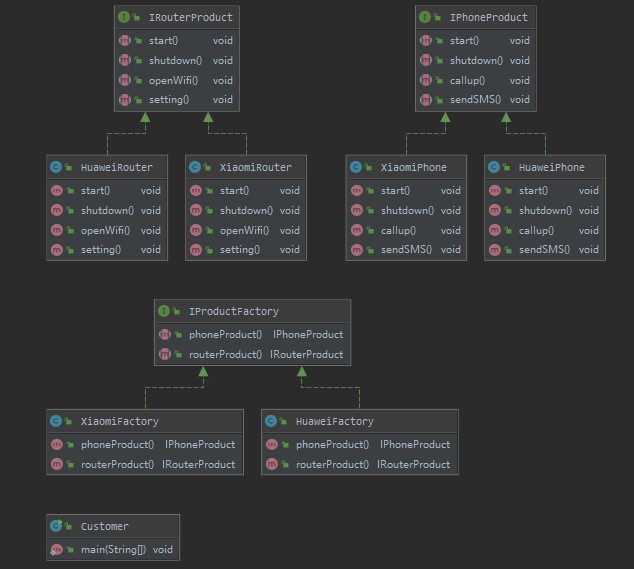
例子: UML类图如下:
抽象工厂模式UML类图.jpg
源码如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 public interface IPhoneProduct void start () void shutdown () void callup () void sendSMS () }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class XiaomiPhone implements IPhoneProduct public void start () System.out.println("小米手机-开机" ); } public void shutdown () System.out.println("小米手机-关机" ); } public void callup () System.out.println("小米手机-打电话" ); } public void sendSMS () System.out.println("小米手机-发短信" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class HuaweiPhone implements IPhoneProduct public void start () System.out.println("华为手机-开机" ); } public void shutdown () System.out.println("华为手机-关机" ); } public void callup () System.out.println("华为手机-打电话" ); } public void sendSMS () System.out.println("华为手机-发短信" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public interface IRouterProduct void start () void shutdown () void openWifi () void setting () }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class XiaomiRouter implements IRouterProduct public void start () System.out.println("小米路由器-开机" ); } public void shutdown () System.out.println("小米路由器-关机" ); } public void openWifi () System.out.println("小米路由器-打开wifi" ); } public void setting () System.out.println("小米路由器-设置" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class HuaweiRouter implements IRouterProduct public void start () System.out.println("华为路由器-开机" ); } public void shutdown () System.out.println("华为路由器-关机" ); } public void openWifi () System.out.println("华为路由器-打开wifi" ); } public void setting () System.out.println("华为路由器-设置" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 public interface IProductFactory IPhoneProduct phoneProduct () ; IRouterProduct routerProduct () ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class XiaomiFactory implements IProductFactory public IPhoneProduct phoneProduct () return new XiaomiPhone(); } public IRouterProduct routerProduct () return new XiaomiRouter(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class HuaweiFactory implements IProductFactory public IPhoneProduct phoneProduct () return new HuaweiPhone(); } public IRouterProduct routerProduct () return new HuaweiRouter(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Customer public static void main (String[] args) System.out.println("======小米======" ); XiaomiFactory xiaomiFactory = new XiaomiFactory(); IPhoneProduct product1 = xiaomiFactory.phoneProduct(); IRouterProduct product2 = xiaomiFactory.routerProduct(); product1.callup(); product1.sendSMS(); product2.openWifi(); product2.setting(); System.out.println("======华为======" ); HuaweiFactory huaweiFactory = new HuaweiFactory(); IPhoneProduct product3 = huaweiFactory.phoneProduct(); IRouterProduct product4 = huaweiFactory.routerProduct(); product3.callup(); product3.sendSMS(); product4.openWifi(); product4.setting(); } }